

Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA)
What is body fat percentage?
Body fat percentage is the proportion of fat in an individual's body. Obesity, a high degree of excess body fat, has been linked to blood pressure, heart disease, diabetes, cancer, and other disabling conditions. Excess body fat has previously been determined by measuring weight against height, but body fat is not always visible and cannot be measured on an ordinary scale.
Body fat percentage measurement.
Body fat scales use the Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA) technique. This method measures body composition by sending a low, safe electrical current through the body. The current passes freely through the fluids in muscle tissue but encounters difficulty/resistance when it passes through fatty tissue. This resistance of the fat tissue to the current is termed 'bioelectrical impedance' and is accurately measured by body fat scales. When set against a person's height, gender and weight, the scales can then compute their body fat percentage. |
 |
Calculation of Body Fat %.
Lukaski & Bolonchuk's (1988)[1] formula for total body water (TBW) is:
- TBW = 0.372(S²÷R) + 3.05(Sex) + 0.142(W) - 0.069(age)
- S = Height in centimetres.
- R = Resistance.
- W = Weight in Kg.
- Sex Male =1 Female = 0.
- Age in years.
Example
An athlete is a male, 25 years old, height 170cm, weight 65kg - measured resistance is 382.
- TBW = 0.372(170² ÷ 382) + 3.05(1) + 0.142(65) - 0.069(25)
- TBW = 38.7kg
The hydration constant of the fat-free mass (FFM) is 0.73, so we can determine the FFM
- FFM = TBW ÷ 0.73 = 38.7 ÷ 0.73 = 53.01 kg
The Fat Mass = Weight - FFM = 65 - 53.01 = 11.99kg
Body Fat % = Fat Mass ÷ Weight x 100 = 11.99 ÷ 65 x 100 = 18.5%
Body fat percentage fluctuations.
Our eating habits, lifestyle and the amount of exercise we perform all affect our weight and hydration levels. Since BIA relies on the fluid levels of 'fat-free mass', such as muscle tissue, certain factors can alter an individual's body fat reading. For example:
- The reading may be lower than normal if you measure your body fat just after a bath or exercise.
- The reading may be higher than normal if you have just woken up or eaten a meal.
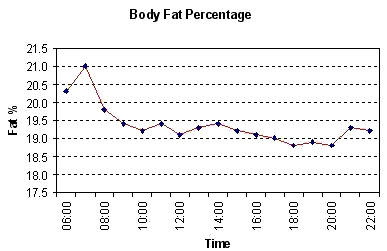
In general, there is less fluctuation in a person's body weight and hydration levels between the late afternoon and the early evening (two hours after eating lunch and before the evening meal). The graph above shows my Body Fat % fluctuations throughout the day.
However, as everyone's daily routine and eating habits are different, you should determine the most suitable time to measure your body fat.
Why monitoring body fat is important.Body fat is vital to daily body functions; it cushions the joints and protects the organs, helps regulate body temperature, stores vitamins and helps the body sustain itself when food is scarce. Everyone needs some body fat to be active and healthy. Most people think that body weight, not body fat, is a direct indicator of fitness. Yet during a diet and exercise regime, while someone's absolute weight may fluctuate, their body fat will decline slowly but steadily to the desired level. Using body fat scales to measure body fat and weight changes gives a more dependable picture of fitness. |
Limitations
Body fat scales only measure the lower part of the body's resistance and may not provide an accurate reading of your body fat.
References
- LUKASKI and BOLONCHUK (1988) Formula for total body water. Aviation Space and Environmental Medicine, 59, p. 1163-1169
Page Reference
If you quote information from this page in your work, then the reference for this page is:
- MACKENZIE, B. (2004) Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA) [WWW] Available from: https://www.brianmac.co.uk/fatbia.htm [Accessed