Body Fat Percentage
Measuring body fat percentage is a method of discovering the correct body weight and composition. Beneath the skin is a layer of subcutaneous fat, and the percentage of total body fat can be measured by taking the 'skinfold' at selected points on the body with a pair of callipers. This test only requires four measurements. A similar alternative method is the Yuhasz skinfold test which requires six measurements.
Objective
This test aims to monitor the athlete's level of body fat.
Required ResourcesTo conduct this test, you will require:
|
 |
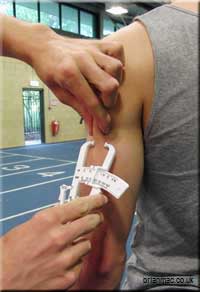
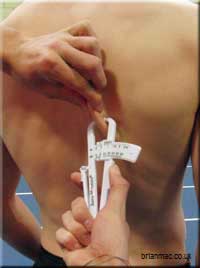
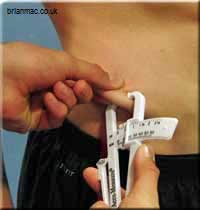
Measurement Sites
The assistant records measurements taken from the following sites:
|
How to conduct the test
|
Fat-free Body Mass & Lean Body Mass
Fat-free body mass (FFBM) represents the body mass devoid of all fat, whereas lean body mass (LBM) contains a small percentage of essential fat.
LBM is a theoretical value developed by Behnke (1974)[2]. For men, Behnke considered it to be FFBM+3% essential fat, and for females, FFBM+12% fat (3% essential fat + 9% sex-specific essential fat).
Fat and Fat-Free Tissue Density
The density of fat and fat-free tissue remains relatively constant: fat = 0.9 gram/cm³ and fat-free tissue = 1.1 gram/cm³.
Typical % Body Fat (Wilmore 1994)[1]
The average man has 15 to 17% body fat, while the average woman is between 18 and 22%. Typical values for elite athletes are 6% to 12% for men and 12% to 20% for women. The following table details the percentage of body fat for male and female athletes for various sports.
| Sport | Male | Female |
| Baseball | 12-16% | 12-19% |
| Basketball | 6-12% | 20-28% |
| Canoeing | 6-12% | 10-16% |
| Cycling | 5-14% | 15-20% |
| Field Hockey | 8-14% | 12-18% |
| Gymnastics | 5-13% | 10-16% |
| Rowing | 6-14% | 12-19% |
| Swimming | 9-13% | 14-24% |
| Tennis | 12-15% | 16-24% |
| Track - Jumpers | 7-11% | 10-18% |
| Track - Runners | 8-10% | 12-19% |
| Track - Throwers | 14-20% | 20-27% |
| Triathlon | 5-11% | 10-15% |
| Volleyball | 11-14% | 16-24% |
Analysis
Analysis of the result is by comparing it with previous tests' results. It is expected that, with appropriate training and diet between each test, the analysis would indicate an improvement in the athlete's body fat percentage.
Target Group
This test is suitable for everyone but not for individuals where the test would be contraindicated.
Reliability
Test reliability refers to how a test is consistent and stable in measuring its intended measure. Reliability will depend upon how strictly the test is conducted. The following link provides various factors influencing the results and test reliability.
Validity
Test validity refers to the degree to which the test measures what it claims to measure and the extent to which inferences, conclusions, and decisions based on test scores are appropriate and meaningful. This test provides a means to monitor training on the athlete's physical development.
The test is not a good predictor of percentage body fat; however, it can indicate changes in body composition over time.
Advantages
- Minimal equipment required.
- Simple to set up and conduct.
- Can be conducted almost anywhere.
Disadvantages
- Specialist equipment required - Skinfold Callipers.
- An assistant is required to administer the test.
References
- WILMORE, J.H. and COSTILL, D.L. (1994) Physiology of sport and exercise. Human Kinetics, Champaign, Illinois
- BEHNKE, A.R. and WILMORE, J.H. (1974) Evaluation and Regulation of Body Build and Composition. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall
Page Reference
If you quote information from this page in your work, then the reference for this page is:
- MACKENZIE, B. (1998) Body fat Percentage [WWW] Available from: https://www.brianmac.co.uk/fatcent.htm [Accessed