

Running Shoes 
With so many different running shoes on the market, it can be challenging to determine which type of shoe you need. Runner's feet come in three styles:
- Pronator (with the heel on the ground, the medial arch is close to the ground)
- Supinator (with the heel on the ground, the medial arch is lifted away from the ground)
- Neutral
What is Pronation?Pronation refers to the inward roll of the foot during normal motion and occurs as the heel's outer edge strikes the ground and the foot rolls inward and flattens out. A moderate amount of pronation is required for the foot to function correctly. However, damage and injury can occur during excessive pronation. When excessive pronation does occur, the foot arch flattens out and stretches the muscles, tendons and ligaments underneath the foot. The picture right shows a view of the right foot as if looking at it from behind. As you can see in the picture, the ankle is overpronating or rolling inwardly. |
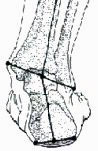 |
What is Supination?In the second picture, right, this time, the foot is supinating or rolling outwardly. Supination is the opposite of pronation and refers to the foot's outward roll during normal motion. Natural supination occurs during the push-off phase of the running gait as the heel lifts off the ground, and the forefoot and toes are used to propel the body forward. However, excessive supination (outward rolling) places a significant strain on the muscles and tendons that stabilize the ankle and can lead to the ankle rolling completely over, resulting in an ankle sprain or total ligament rupture. |
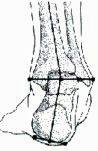 |
How do you determine your style?
If you have an old pair of running shoes, place them on a flat surface. If they lean outwards from each other, you are a supinator. If they lean inwards, a pronator. Otherwise, you are neutral. Alternatively, walk on a tiled floor with wet feet. If the wet strip's width connecting the heel to the toes is more than half the foot width, you are a pronator, less than half the width, a supinator; otherwise, you are neutral.
Type of shoes
The shoe types available are:
- Motion control.
- Cushion/motion control.
- Support.
- Cushion.
- Lightweight/supportive.
- Lightweight.
- Racer/supportive.
- Racer.
- Trail.
There are many sites providing information on the best running shoes in various categories according to their testing experience and thousands of visitors' feedback. In choosing your running shoes, you also need to take into consideration your weight and the running you will be doing:
- Steady road running.
- Fast road running.
- Road racing.
- Road and trail running.
Advise
If your foot type is supinator or pronator and you have a coach, ask them to look at how you run. Some athletes may need inserts in their shoes to correct overpronation and may require a gait assessment by a podiatrist (foot specialist).
Rules for Track Shoes
IAAF Competition Rules 142 states:
- The shoes' soles and heels shall be constructed to provide up to 11 spikes. Any number of spikes up to 11 may be used, but the number of spike positions shall not exceed 11.
- When a competition is conducted on a synthetic surface, that part of each spike that projects from the sole or the heel shall not exceed 9mm except in the high jump and javelin throw events, where it shall not exceed 12mm. These spikes shall have a maximum diameter of 4mm.
- For the non-synthetic surfaces, the maximum length of the spike shall be 25mm, and the maximum diameter is 4mm.
- The sole and heel may have grooves, ridges, indentations or protrusions, provided these features are constructed of the same or similar material to the basic sole. In the high jump and long jump, the sole shall have a maximum thickness of 13mm and the heel in the high jump shall have a maximum thickness of 19mm. The sole and heel may be of any thickness in all other events.
Shoe Care
To reduce damage to your running shoes:
- Only wear them for running and do not use them for playing other sports.
- Undo the laces before removing the shoes.
- Avoid running in wet shoes.
- Please do not wash them in the washing machine.
- Do not expose them to excessive heat - let them dry naturally.
Shoe Life
-
The midsole material in most running shoes may lose 30-50% of its shock absorption after approx. 250 miles of use - consider replacing your shoes after 500 miles of use.
Page Reference
If you quote information from this page in your work, then the reference for this page is:
- MACKENZIE, B. (2000) Running Shoes [WWW] Available from: https://www.brianmac.co.uk/shoes.htm [Accessed